汽车检测
以下为udacity的SDCND的一个项目
ps:这里使用的是用opencv进行特征提取+svm分类器的方法实现物体检测,是在深度学习流行前比较经典的实现方法
项目描述:
使用openCV提取图片特征,训练svm分类器,分类车辆与非车辆。用训练好的模型识别汽车前置摄像头记录视频中的车辆。
代码github地址:yang1688899/CarND-Vehicle-Detection
车辆非车辆数据:https://pan.baidu.com/s/13nCrYRdeK7TydsUiDiuHNA
实现步骤:
- 分析训练数据,提取图片HOG特征。
- 训练分类器
- 应用滑动窗口(sliding windows)实现车辆检测
- 应用热力图(heatMap)过滤错误检测(false positive)
分析训练数据,提取图片HOG特征
训练数据为64x64x3的RBG图片,包含车辆与非车辆图片两类,车辆图片8792张,非车辆图片8968张。 以下为车辆,非车辆图片样例:

提取HOG特征,以下为实现方法:
# Define a function to return HOG features and visualization
def get_hog_features(img, orient, pix_per_cell, cell_per_block, vis=False, feature_vec=True):
if vis == True:
features, hog_image = hog(img, orientations=orient, pixels_per_cell=(pix_per_cell, pix_per_cell),
cells_per_block=(cell_per_block, cell_per_block), transform_sqrt=False,
visualise=True, feature_vector=False)
return features, hog_image
else:
features = hog(img, orientations=orient, pixels_per_cell=(pix_per_cell, pix_per_cell),
cells_per_block=(cell_per_block, cell_per_block), transform_sqrt=False,
visualise=False, feature_vector=feature_vec)
return features
以下为原图与提取的HOG特征图对比:

训练分类器
这里使用SVM分类器,以下为代码:
t = time.time()
car_features = utils.extract_features(cars, cspace=colorspace, orient=orient,
pix_per_cell=pix_per_cell, cell_per_block=cell_per_block,
hog_channel=hog_channel)
notcar_features = utils.extract_features(notcars, cspace=colorspace, orient=orient,
pix_per_cell=pix_per_cell, cell_per_block=cell_per_block,
hog_channel=hog_channel)
t2 = time.time()
print(round(t2-t, 2), 'Seconds to extract features...')
# Create an array stack of feature vectors
X = np.vstack((car_features, notcar_features))
X = X.astype(np.float64)
# Fit a per-column scaler
# X_scaler = StandardScaler().fit(X)
# Apply the scaler to X
# scaled_X = X_scaler.transform(X)
# Define the labels vector
y = np.hstack((np.ones(len(car_features)), np.zeros(len(notcar_features))))
# Split up data into randomized training and test sets
rand_state = np.random.randint(0, 100)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=rand_state)
print('Feature vector length:', len(X_train[0]))
# Use a linear SVC
svc = LinearSVC()
# Check the training time for the SVC
t = time.time()
svc.fit(X_train, y_train)
t2 = time.time()
t2 = time.time()
print(round(t2-t, 2), 'Seconds to train classfier...')
# Check the score of the SVC
print('Test Accuracy of classfier = ', round(svc.score(X_test, y_test), 4))
# Check the prediction time for a single sample
t=time.time()
n_predict = 10
print('My classfier predicts: ', svc.predict(X_test[0:n_predict]))
print('For these',n_predict, 'labels: ', y_test[0:n_predict])
t2 = time.time()
print(round(t2-t, 5), 'Seconds to predict', n_predict,'labels with classfier')
最终训练的分类器在测试数据集得到98.0%准确率
应用滑动窗口(sliding windows)实现车辆检测
由于提取HOG特征比较耗时,先直接提取整张图片的HOG特征,然后获取每个窗口所属的那部分HOG特征,这样效率会更高,以下为滑动窗口搜索的代码实现:
# Define a single function that can extract features using hog sub-sampling and make predictions
def find_cars(img, ystart, ystop, scale, cspace, hog_channel, svc, X_scaler, orient,
pix_per_cell, cell_per_block, spatial_size, hist_bins, show_all_rectangles=False):
# array of rectangles where cars were detected
windows = []
img = img.astype(np.float32) / 255
img_tosearch = img[ystart:ystop, :, :]
# apply color conversion if other than 'RGB'
if cspace != 'RGB':
if cspace == 'HSV':
ctrans_tosearch = cv2.cvtColor(img_tosearch, cv2.COLOR_RGB2HSV)
elif cspace == 'LUV':
ctrans_tosearch = cv2.cvtColor(img_tosearch, cv2.COLOR_RGB2LUV)
elif cspace == 'HLS':
ctrans_tosearch = cv2.cvtColor(img_tosearch, cv2.COLOR_RGB2HLS)
elif cspace == 'YUV':
ctrans_tosearch = cv2.cvtColor(img_tosearch, cv2.COLOR_RGB2YUV)
elif cspace == 'YCrCb':
ctrans_tosearch = cv2.cvtColor(img_tosearch, cv2.COLOR_RGB2YCrCb)
else:
ctrans_tosearch = np.copy(img)
# rescale image if other than 1.0 scale
if scale != 1:
imshape = ctrans_tosearch.shape
ctrans_tosearch = cv2.resize(ctrans_tosearch, (np.int(imshape[1] / scale), np.int(imshape[0] / scale)))
# select colorspace channel for HOG
if hog_channel == 'ALL':
ch1 = ctrans_tosearch[:, :, 0]
ch2 = ctrans_tosearch[:, :, 1]
ch3 = ctrans_tosearch[:, :, 2]
else:
ch1 = ctrans_tosearch[:, :, hog_channel]
# Define blocks and steps as above
nxblocks = (ch1.shape[1] // pix_per_cell) + 1 # -1
nyblocks = (ch1.shape[0] // pix_per_cell) + 1 # -1
nfeat_per_block = orient * cell_per_block ** 2
# 64 was the orginal sampling rate, with 8 cells and 8 pix per cell
window = 64
nblocks_per_window = (window // pix_per_cell) - 1
cells_per_step = 2 # Instead of overlap, define how many cells to step
nxsteps = (nxblocks - nblocks_per_window) // cells_per_step
nysteps = (nyblocks - nblocks_per_window) // cells_per_step
# Compute inpidual channel HOG features for the entire image
hog1 = utils.get_hog_features(ch1, orient, pix_per_cell, cell_per_block, feature_vec=False)
if hog_channel == 'ALL':
hog2 = utils.get_hog_features(ch2, orient, pix_per_cell, cell_per_block, feature_vec=False)
hog3 = utils.get_hog_features(ch3, orient, pix_per_cell, cell_per_block, feature_vec=False)
for xb in range(nxsteps):
for yb in range(nysteps):
ypos = yb * cells_per_step
xpos = xb * cells_per_step
# Extract HOG for this patch
hog_feat1 = hog1[ypos:ypos + nblocks_per_window, xpos:xpos + nblocks_per_window].ravel()
if hog_channel == 'ALL':
hog_feat2 = hog2[ypos:ypos + nblocks_per_window, xpos:xpos + nblocks_per_window].ravel()
hog_feat3 = hog3[ypos:ypos + nblocks_per_window, xpos:xpos + nblocks_per_window].ravel()
hog_features = np.hstack((hog_feat1, hog_feat2, hog_feat3))
else:
hog_features = hog_feat1
xleft = xpos * pix_per_cell
ytop = ypos * pix_per_cell
test_prediction = svc.predict(hog_features)
if test_prediction == 1 or show_all_rectangles:
xbox_left = np.int(xleft * scale)
ytop_draw = np.int(ytop * scale)
win_draw = np.int(window * scale)
windows.append(
((xbox_left, ytop_draw + ystart), (xbox_left + win_draw, ytop_draw + win_draw + ystart)))
return windows
车辆由于距离远近不同会在视频呈现的不一样的大小且出现的位置也会各异,这里使用4类不同大小的滑动窗口对图片中的车辆进行搜索:
第一类大小为64x64,重叠率(overlap)为0.75,用来检测距离较远的车辆:
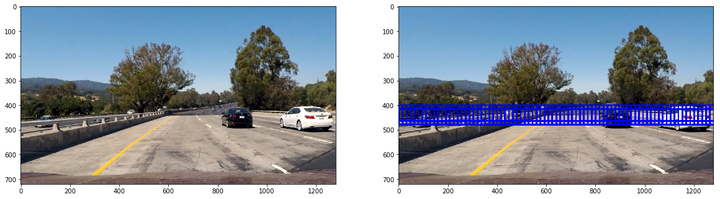
第二类大小为96x96,重叠率(overlap)为0.75,用来检测中距离车辆:
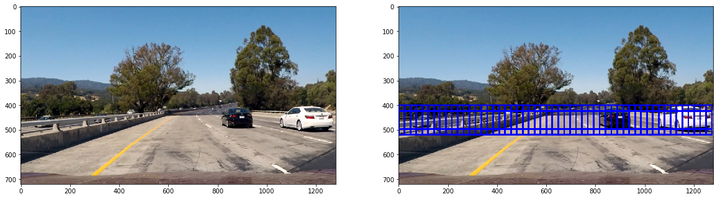
第三类大小为128x128,重叠率(overlap)为0.75,用来检测近距离车辆:
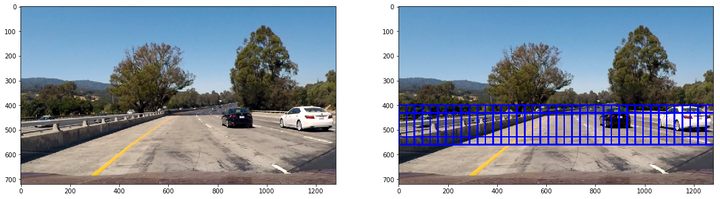
第四类大小为224x224,重叠率(overlap)为0.75,用来检测极近距离车辆:
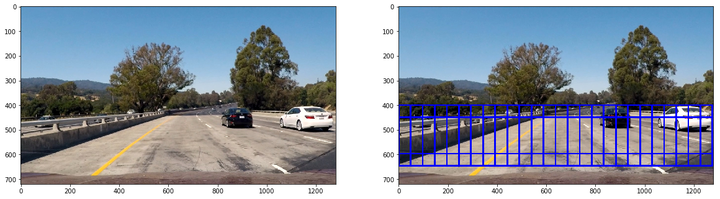
应用在测试图片得到的下列结果:
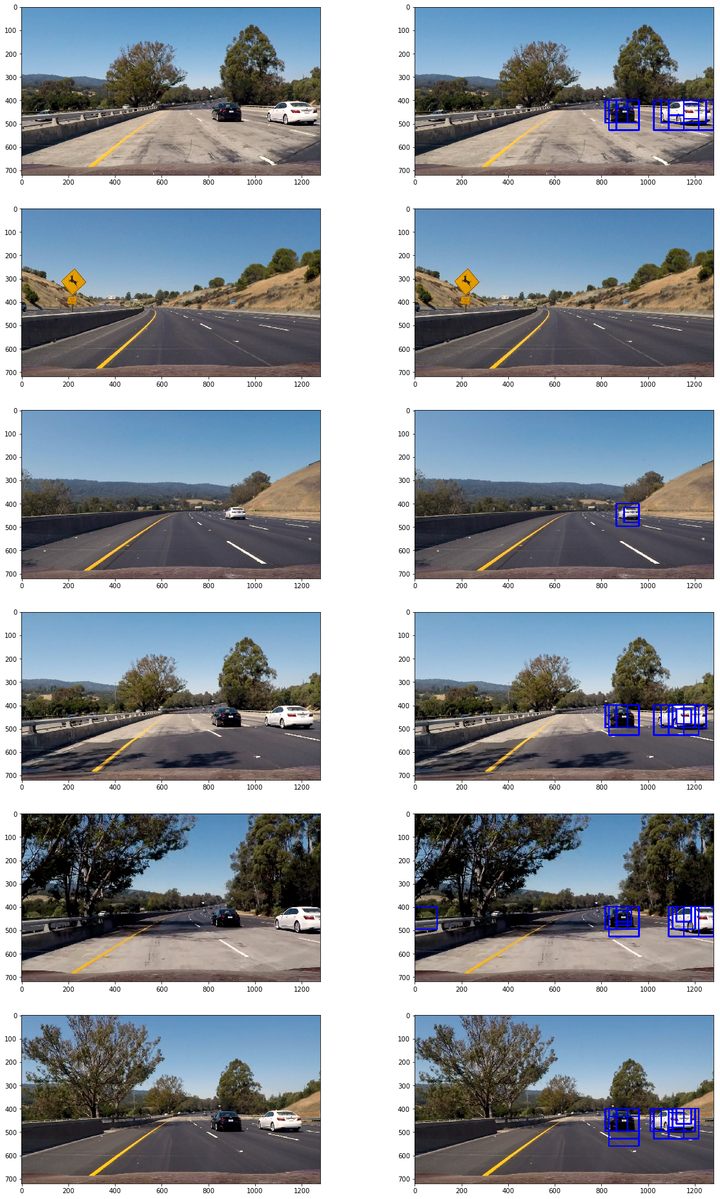

可以看到存在一些多窗口重合及错误检测(false positive)现象
应用热图(heatMap)过滤错误检测(false positive)
由于使用多个大小不一滑动窗口,且窗口存在重叠,单个车辆图像会被多个窗口捕捉检测。使用这个现象可以过滤错误检测。
记录一张图片上所有positive detections,使用记录的positive detections形成一个检测热图:
def add_heat(heatmap, bbox_list):
# Iterate through list of bboxes
for box in bbox_list:
# Add += 1 for all pixels inside each bbox
# Assuming each "box" takes the form ((x1, y1), (x2, y2))
heatmap[box[0][1]:box[1][1], box[0][0]:box[1][0]] += 1
以下应用在测试图片得到的检测热图:
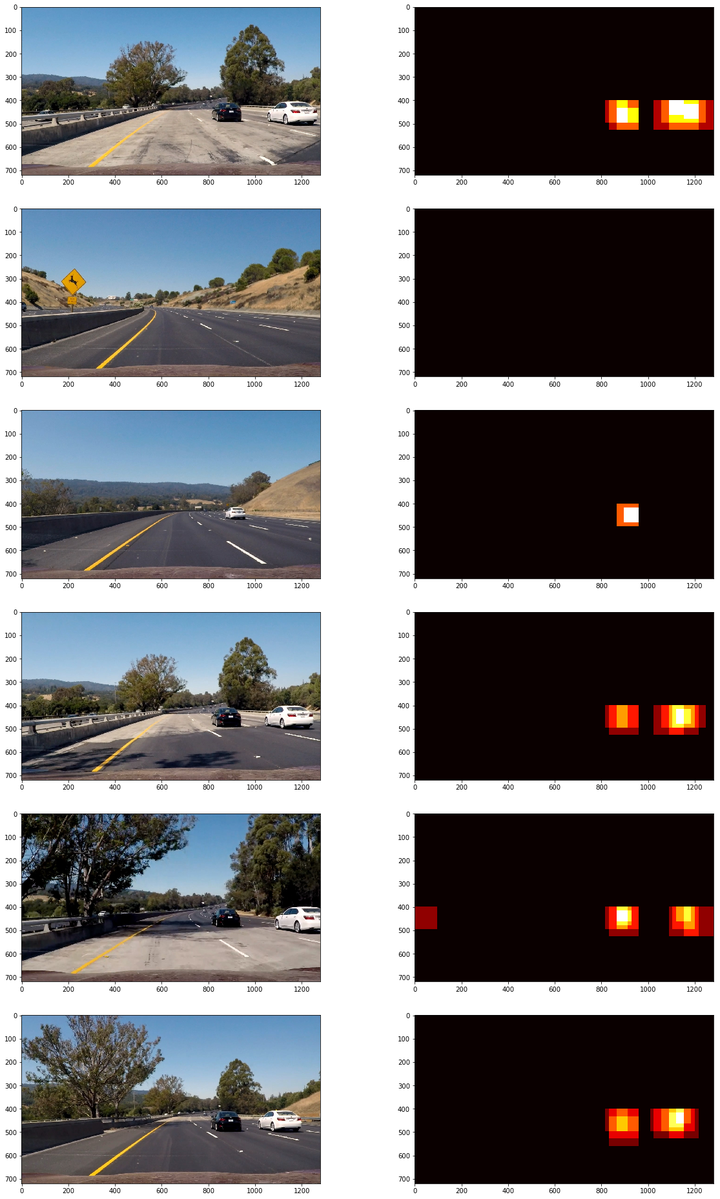
然后对热图进行阈值过滤,过滤错误检测,以下为阈值过滤实现代码:
def apply_threshold(heatmap, threshold):
# Zero out pixels below the threshold
heatmap[heatmap <= threshold] = 0
# Return thresholded map
return heatmap
以下为整个pipeline应用在测试图片的效果:
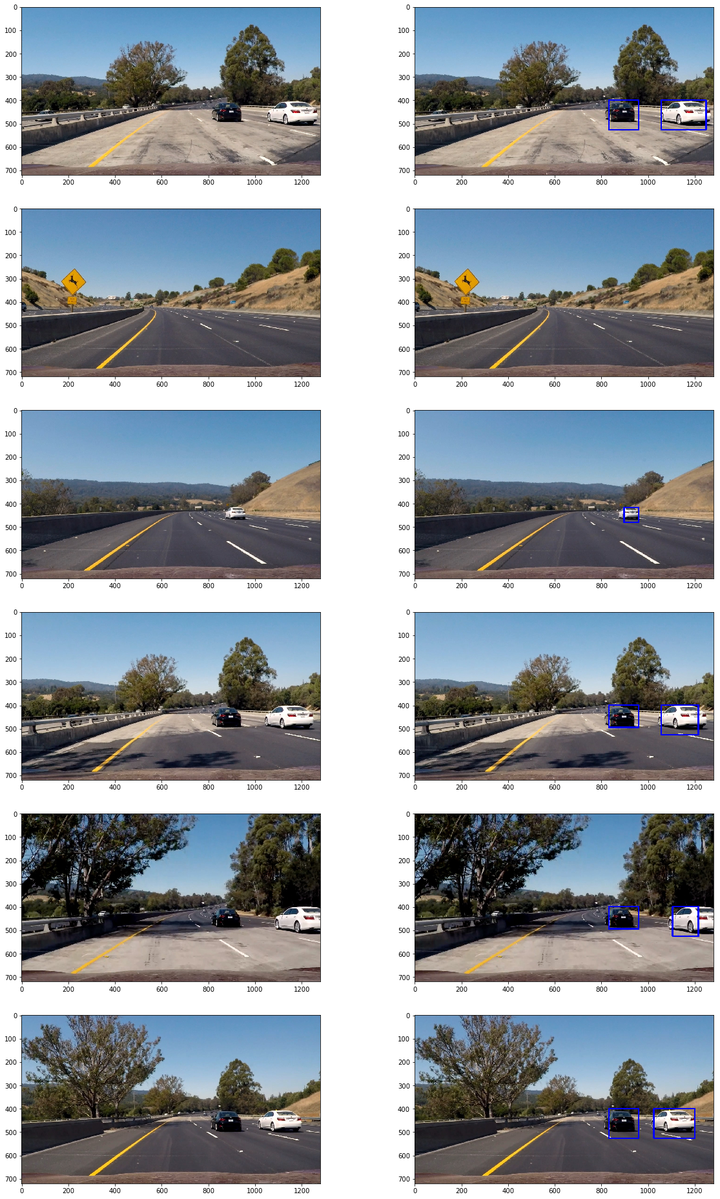

相关阅读
其实12306抢票之前有做过,近年来随着技术的发展AI的兴起,我也随波逐流,研究了下python深度学习,来实现12306全自动抢票工具。 1. 实现
图像特征包括颜色特征、纹理特征、形状特征以及局部特征点等。局部特点具有很好的稳定性,不容易受外界环境的干扰。 1. 局部特征点
Oracle 11g ORA-12514:TNS:监听程序当前无法识别连接
使用PL/SQL登录Oracle数据库,提示【ORA-12514:TNS:监听程序当前无法识别连接描述符中请求的服务】如下图: 直接上解决办法哈: 一:看
无论我们有多少年的网龄、站龄,对于如今类似房地产一样爆发的域名市场着实的搞不清。有些当初持有不少当时看似毫无价值的域名,如今
得益于移动设备和数码摄像的高速发展,人脸识别技术突飞猛进,已经成为多项产品的主要应用支撑或重要配置。本文对目前人脸识别的三种